
The superior speed of ADB
When comparing various methods of pathogen eradication that are available in the marketplace, a very important factor to consider is speed. Speed is critical. If an infected person enters a space and releases a dangerous virus into the air, the speed in which the system inactivates the virus is of the utmost importance. Air Disinfection Biosecurity (patent pending) technology works tremendously faster than other methods in the market.
The transmission of viruses and bacteria can be vastly diminished by the fact that these pathogens are neutralized so quickly by ADB. In laboratory testing, a SARS-CoV-2 surrogate was reduced by 90 percent in 16 seconds, and by 99.9 percent in 30 seconds using ADB.
The charts below, from an independent third party testing laboratory, show how well ADB units perform against other common methods. ADB achieved a 3-log reduction rate (99.9 percent reduction) significantly faster than the rest. Note: These results were done in a 2,640 cubic foot room (22 foot width x 12 foot length x 10 foot height). Real world results can vary.
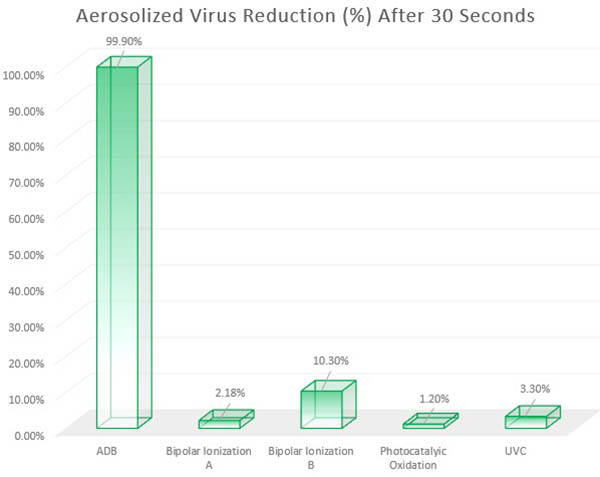
Aerosolized Viruses: ADB achieved a 99.9 percent reduction in about 30 seconds. The next fastest method was bipolar ionization (BPI-2), which took nearly 10 minutes to achieve 99.9 percent. Click here to download curve chart. ADB is represented on the curve charts as "MDBD," for "Modulated Dielecric Barrier Discharge."
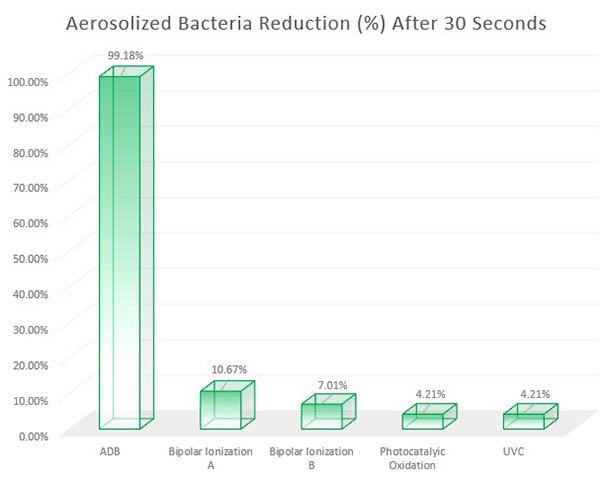
Aerosolized Bacteria: ADB achieved a 99.9 percent reduction in just under a minute. Click here to download curve chart. ADB is represented on the curve charts as "MDBD," for "Modulated Dielecric Barrier Discharge."
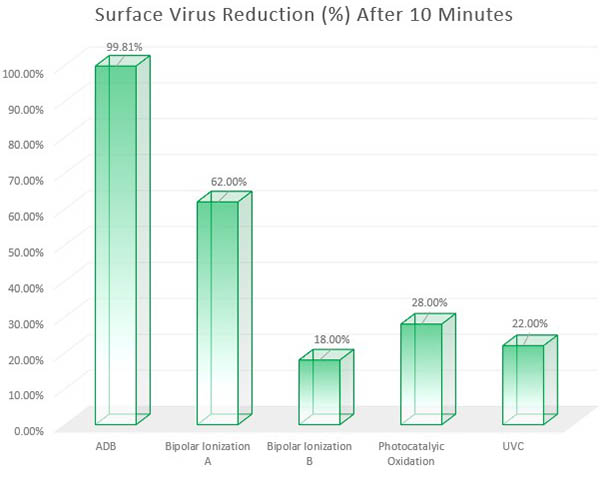
Viruses on Surfaces (Stainless Steel, Plastic, Linoleum, and Fabric): ADB achieved a 99.9 percent reduction in just over 10 minutes. Click here to download curve chart. ADB is represented on the curve charts as "MDBD," for "Modulated Dielecric Barrier Discharge."
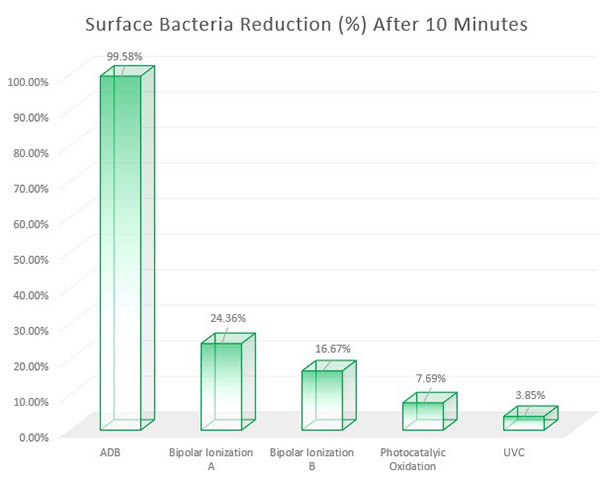
Bacteria on Surfaces (Stainless Steel, Plastic, Linoleum, and Fabric): ADB achieved a 99.9 percent reduction in about 10-12 minutes. Click here to download curve chart. ADB is represented on the curve charts as "MDBD," for "Modulated Dielecric Barrier Discharge."
The faster, the better
Consider this - the typical person exhales about 0.25 cubic feet of air in one minute. In the 16 seconds required for ADB to inactivate 90 percent of an airborne virus, that translates to just 0.07 cubic feet of air. This leaves only 0.007 cubic feet of infected air that can possibly create transmission of the virus. Fourteen seconds later, even that is virtually all mitigated, with the reduction percentage being 99.9 percent in 30 seconds. Due to the speed in which ADB can inactivate viruses like SARS-CoV-2, this severely limits the chances of transmission from person to person.